Linear Alkyl Benzene (LAB)
Linear Alkyl Benzene (LAB)
In this article, we will discuss the nature of Linear Alkyl Benzene, and its specific features. It is also intended to provide the readers with efficient information on various types of Linear Alkyl Benzene, their unique characteristics, and applications. Moreover, it provides a brief explanation about Iran’s LAB production.
What is Linear Alkyl Benzene?
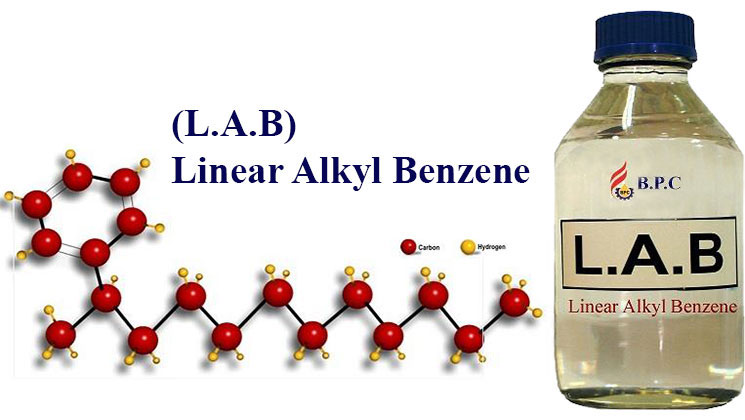
Linear alkyl benzene (LAB) is a colorless to pale yellow liquid that emits a strong, characteristic odor. It is composed of a complex mixture of predominantly linear and mono-alkylated isomers of alkyl benzenes. Linear alkyl benzene is a crucial organic compound extensively utilized in the production of biodegradable detergents. It belongs to the family of alkyl benzenes that are derived from linear olefins, obtained from crude oil or natural gas. The process of producing LAB involves the reaction of linear olefins with benzene, using a catalyst such as hydrofluoric acid or aluminum chloride. The resulting product is then subjected to purification and distillation processes to obtain the final high-quality LAB product.
It is a type of colorless liquid that is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and acetone. It has a high boiling point and remains stable under normal conditions. The primary application of LAB is as a surfactant in detergents owing to its exceptional ability to reduce the surface tension of water and enhance the cleaning performance of the detergent. Apart from this, it finds extensive usage in other domains such as lubricants, solvents, and agricultural chemicals.
Linear Alkyl Benzene’s specific features
Linear Alkyl Benzene is a type of organic compound that has some features. The molecular structure of LAB is characterized by an aromatic hydrocarbon comprising a benzene ring and a linear alkyl chain that is attached to it. The length of the alkyl chain may differ, but it usually consists of 10 to 14 carbon atoms. It is a clear liquid that exhibits insolubility in water but solubility in organic solvents like benzene and toluene. After Sulfonation in downstream processing units, LAB is changed to Linear ALkyl Benzene Sulfonate Acid (LABSA) and it is used as the primary cleaning agent in household detergents including cleaning powders and liquids.
Click on the link below to read more:
Comments
Post a Comment